オイラーグラフとオイラー閉路
グラフ上の任意の頂点から出発して、すべての辺を使って一筆書きをすることができるようなグラフを準オイラーグラフと呼びます。またそのような一筆書きの順番で頂点を並べたパスをオイラー路と呼びます。ここでは始点と終点が同じ頂点である必要はありません。
これに対して一筆書きができるだけでなく、最初の頂点に戻ることができるようなグラフをオイラーグラフと呼びます。そしてそのような一筆書きの順番で頂点を並べたパスをオイラー閉路と呼びます。
一筆書きが可能かどうかは簡単な方法でわかります。まずすべての頂点が連結していることです。そして各頂点から出ている辺の数が奇数であるものが存在しないか 2個だけである場合です。各頂点から出ている辺の数がすべて偶数の場合、一筆書きが可能であり、始点と終点は同じ頂点になります。奇数である頂点が2つある場合は一方が始点となり、もう片方が終点となります。
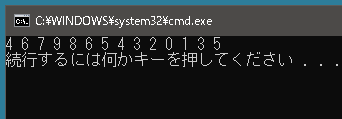
頂点が10個あり、以下のような辺を持つグラフがあったとします。
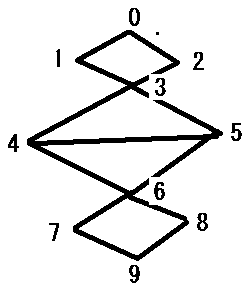
このようなテキストファイルを用意します。1行目が頂点数で、2行目以降がどの頂点同士がつながっているのかを示しています。またこれは無向グラフです。「0 1」ということは 0 から 1 へつながっているとともに 1 から 0 へもつながっています。
example.txt
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
10 0 1 0 2 1 3 2 3 3 4 3 5 4 5 4 6 6 8 6 7 5 6 7 9 8 9 |
まずテキストファイルのデータを読み出して、どの頂点がどの頂点につながっているのかを調べます。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 |
public class Program { static List<int>[] GetAdjacencyListFromFile(string filePath, bool isDirectedGraph) { System.IO.StreamReader sr = new System.IO.StreamReader(filePath); string str = sr.ReadToEnd(); sr.Close(); str = str.Replace("\r", ""); string[] arr = str.Split(new string[] { "\n" }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries); int vertexCount = int.Parse(arr[0]); // 1行目は頂点の数 List<int>[] adjacencyList = new List<int>[vertexCount]; // 2行目は辺の情報 for (int i = 0; i < vertexCount; i++) adjacencyList[i] = new List<int>(); for (int i = 1; i < arr.Length; i++) { int[] sg = arr[i].Split().Select(_ => int.Parse(_)).ToArray(); adjacencyList[sg[0]].Add(sg[1]); if(!isDirectedGraph) adjacencyList[sg[1]].Add(sg[0]); } return adjacencyList; } static void Main() { // 有向グラフなら第二引数をtrueにすること List<int>[] adjacencyList = GetAdjacencyListFromFile("ファイルのパス", false); EulerGraph eulerGraph = new EulerGraph(); // それからどうするか?? } } |
EulerGraphクラスの定義
オイラー路を取得する処理をおこなうためのEulerGraphクラスを定義します。オイラー路を取得するまえに、本当にオイラー路が存在するのかを確認しなければなりません。
一筆書きは可能なのか?
一筆書きが可能であるためには、すべての頂点が連結していなければなりません。それを確認するためには、深さ優先探索(幅優先探索でもよい)で任意の頂点から各頂点にたどり着けるかを調べます(厳密には、グラフが準オイラーグラフであるための連結性の条件は「孤立点を除いたグラフが連結である」ですが、ここでは孤立点があるかどうかは考えない)。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
public class EulerGraph { public bool IsGraphConnected(List<int>[] adjacencyList) { bool[] isVisits = new bool[adjacencyList.Length]; isVisits[0] = true; Stack<int> stack = new Stack<int>(); stack.Push(0); while (stack.Count > 0) { int cur = stack.Pop(); foreach (int i in adjacencyList[cur]) { if (isVisits[i]) continue; stack.Push(i); isVisits[i] = true; } } if (isVisits.Any(_ => _ == false)) return false; else return true; } } |
次に頂点の次数(頂点から出ている辺の数)が奇数のものを数えます。0なら一筆書きが可能で始点終点は同じなので始点も終点も0にします。2なら一筆書きが可能で一方が始点であり、もう片方が終点なのでstartとgoalは異なる奇数点の番号を格納します。それ以外のときは一筆書きはできないのでfalseを返します。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 |
public class EulerGraph { bool IsEulerGraph(List<int>[] adjacencyList, ref int start, ref int goal) { if (!IsGraphConnected(adjacencyList)) return false; // 奇数点を数える int count = adjacencyList.Count(_ => _.Count % 2 == 1); if (count == 0) { start = 0; goal = 0; return true; } else if (count == 2) { start = -1; goal = -1; for (int i = 0; i < adjacencyList.Length; i++) { if (adjacencyList[i].Count % 2 == 1) { if (start == -1) start = i; else if (goal == -1) goal = i; } } return true; } else return false; } } |
有向グラフの場合は、すべての頂点において入次数と出次数が同じであるか、(入次数 + 1 = 出次数)のものと(入次数 = 出次数 + 1)がそれぞれひとつずつ存在する場合でないと一筆書きはできません。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 |
public class EulerGraph { public bool IsEulerGraph2(List<int>[] adjacencyList, ref int start, ref int goal) { if (!IsGraphConnected(adjacencyList)) return false; int[] outCount = new int[adjacencyList.Length]; int[] inCount = new int[adjacencyList.Length]; for (int i = 0; i < adjacencyList.Length; i++) { outCount[i] = adjacencyList[i].Count; for (int m = 0; m < adjacencyList[i].Count; m++) { int goal2 = adjacencyList[i][m]; inCount[goal2]++; } } start = -1; goal = -1; for (int i = 0; i < adjacencyList.Length; i++) { if (outCount[i] != inCount[i]) { //(入次数 + 1 = 出次数)のものと(入次数 = 出次数 + 1)がそれぞれひとつだけ存在する // 複数存在したり片方しか存在しない場合は不可 if (outCount[i] == inCount[i] + 1 && start == -1) start = i; else if (outCount[i] + 1 == inCount[i] && goal == -1) goal = i; else return false; } } // すべての頂点で入次数と出次数が同じ if (start == -1 && goal == -1) { start = 0; goal = 0; } if (start != -1 && goal != -1) return true; else return false; } } |
深さ優先探索でオイラー路を取得する
始点がどこになるのかが分かったら深さ優先探索でオイラー路を取得します。試しに深さ優先探索で行き止まりになるまで進み続けて取得した結果を表示させてみます。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
public class Program { static void Main() { List<int>[] adjacencyList = GetAdjacencyListFromFile("ファイルのパス", false); EulerGraph eulerGraph = new EulerGraph(); eulerGraph.Test(adjacencyList); } } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 |
public class EulerGraph { public void Test(List<int>[] adjacencyList) { int start = 0, goal = 0; IsEulerGraph(adjacencyList, ref start, ref goal); Console.WriteLine("始点:" + start); Console.WriteLine("終点:" + goal); int prevIndex = -1; Stack<int> nextIndexs = new Stack<int>(); Stack<int> prevIndexs = new Stack<int>(); nextIndexs.Push(start); prevIndexs.Push(-1); List<List<int>> pathList = new List<List<int>>(); List<int> path = new List<int>(); // 深さ優先探索で行き止まりになるまで進み続ける while (nextIndexs.Count > 0) { int curIndex = nextIndexs.Pop(); prevIndex = prevIndexs.Pop(); if (prevIndex != -1) { // 一度通った辺は通らないのでRemoveする // すでに存在しない場合は探索していたパスとは別のパスの探索が始まった場合である if (!adjacencyList[prevIndex].Remove(curIndex)) continue; // 無向グラフの場合は逆向きの辺も同時にRemoveする adjacencyList[curIndex].Remove(prevIndex); path.Add(prevIndex); } List<int> nexts = adjacencyList[curIndex]; foreach (int i in nexts) { // 次回の訪問対象と今回訪問した頂点をスタックに保存する nextIndexs.Push(i); prevIndexs.Push(curIndex); } if (nexts.Count == 0) { // 次回の訪問対象が存在しない場合は行き止まりまで探索されたことを意味する path.Add(curIndex); pathList.Add(path); // ためしに表示させてみる Console.WriteLine("行き止まり:深さ優先探索の結果:" + string.Join(" ", path)); path = new List<int>(); } } } } |
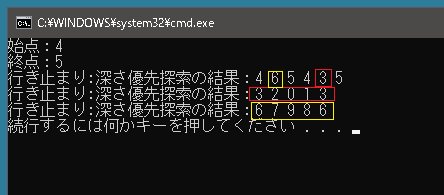
途中で選択する辺を間違えた場合、選択すべき部分の探索は行き止まりになってから行なわれます。そこでその部分はあとでつなぎかえることにします。
完成させる
GetResultDfsメソッドを定義して、これが返したリストのリストをつなぎかえてオイラー路を取得します。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 |
public class EulerGraph { public List<int> GetEulerPath(List<int>[] adjacencyList, bool isDirectedGraph) { int start = 0, goal = 0; // adjacencyListをそのまま渡すと改ざんされてしまうのでコピーを作って渡す List<int>[] copiedList = new List<int>[adjacencyList.Length]; for (int i = 0; i < adjacencyList.Length; i++) copiedList[i] = adjacencyList[i].ToList(); bool isEulerGraph; if (isDirectedGraph) isEulerGraph = IsEulerGraph2(adjacencyList, ref start, ref goal); else isEulerGraph = IsEulerGraph(adjacencyList, ref start, ref goal); if (isEulerGraph) { // 深さ優先探索で行き止まりになるまで進み続けて得られる結果を取得して List<List<int>> results = GetResultDfs(copiedList, start, isDirectedGraph); // 最後に連結する return JoinResults(results); } else return new List<int>(); } List<List<int>> GetResultDfs(List<int>[] adjacencyList, int start, bool isDirectedGraph) { int prevIndex = -1; Stack<int> nextIndexs = new Stack<int>(); Stack<int> prevIndexs = new Stack<int>(); nextIndexs.Push(start); prevIndexs.Push(-1); List<List<int>> pathList = new List<List<int>>(); List<int> path = new List<int>(); // 深さ優先探索 while (nextIndexs.Count > 0) { int curIndex = nextIndexs.Pop(); prevIndex = prevIndexs.Pop(); if (prevIndex != -1) { if (!adjacencyList[prevIndex].Remove(curIndex)) continue; if(!isDirectedGraph) adjacencyList[curIndex].Remove(prevIndex); path.Add(prevIndex); } List<int> nexts = adjacencyList[curIndex]; foreach (int i in nexts) { nextIndexs.Push(i); prevIndexs.Push(curIndex); } if (nexts.Count == 0) { path.Add(curIndex); pathList.Add(path); path = new List<int>(); } } return pathList; } List<int> JoinResults(List<List<int>> results) { List<int> result = new List<int>(); result = results[0]; if (results.Count > 1) { for (int i = 1; i < results.Count; i++) { int target = results[i][0]; int targetIndex = result.IndexOf(target); result.Skip(targetIndex + 1).ToList(); List<int> temp = new List<int>(); temp.AddRange(result.Take(targetIndex).ToList()); temp.AddRange(results[i]); temp.AddRange(result.Skip(targetIndex + 1)); result = temp; } } return result; } } |
定義したEulerGraph.GetEulerPathメソッドでオイラー路を表示させてみることにします。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
public class Program { static void Main() { // 有向グラフなら第二引数をtrueにすること List<int>[] adjacencyList = GetAdjacencyListFromFile("ファイルのパス", false); EulerGraph eulerGraph = new EulerGraph(); List<int> result = eulerGraph.GetEulerPath(adjacencyList, false); if (result.Count != 0) Console.WriteLine(string.Join(" ", result)); else Console.WriteLine("一筆書きはできません"); } } |